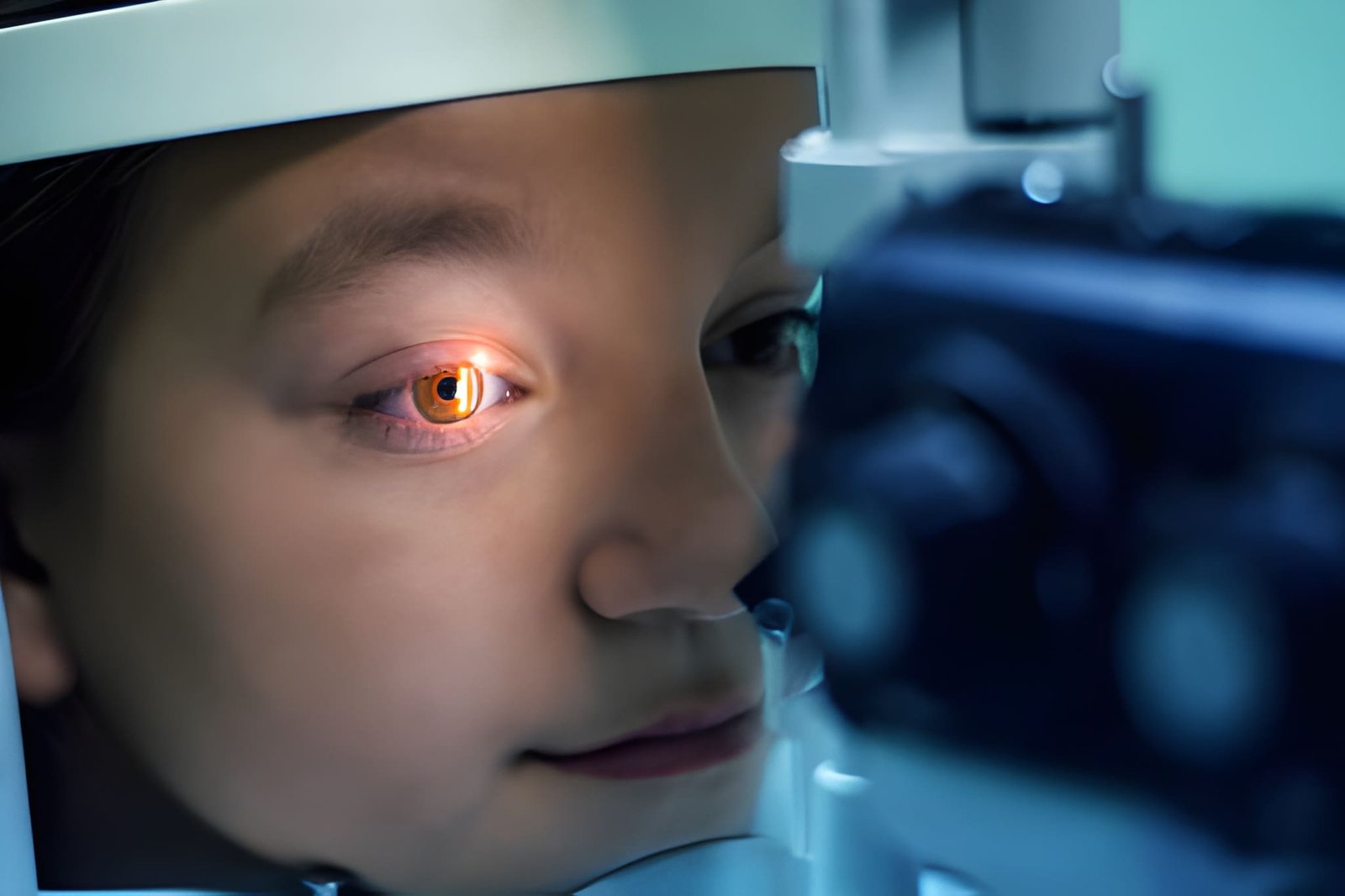
Childhood eye problems encompass a wide range of conditions that can affect visual health and development. From common refractive errors like nearsightedness and farsightedness to more complex issues such as amblyopia and strabismus, these conditions can impact a child’s ability to learn, socialize, and thrive. Recognizing the underlying factors contributing to childhood eye problems is essential for early detection and intervention. By understanding the causes, parents, caregivers, and healthcare providers can implement strategies to prevent, manage, and treat these issues effectively, ensuring optimal eye health and visual outcomes for children.
Book Appointment With Dr. Qasim
Concerned about your child’s eye health? Consult with Dr. Qasim, a trusted pediatric ophthalmologist in Dubai, for personalized care and expert guidance. Schedule an appointment today to prioritize your child’s vision and well-being. Trust Dr. Qasim for comprehensive eye care solutions tailored to your child’s needs.
Book Appointment With DR. Qasim
Developmental Factors
Children’s eyes undergo significant changes and growth during infancy and childhood. The visual system continues to develop and mature, making children more susceptible to certain eye problems such as refractive errors, amblyopia, and strabismus. Developmental milestones in the visual system can be accompanied by various eye problems. Refractive errors, such as myopia and hyperopia, often emerge during childhood due to changes in the shape and length of the eyeball. Amblyopia, or “lazy eye,” can develop if there is a disruption in visual development during early childhood. Strabismus, characterized by misalignment of the eyes, can also arise during this critical period of visual development.
Genetic Factors
Many eye problems in children have a genetic component, meaning they are passed down from parents to their offspring. Conditions like congenital cataracts, glaucoma, and retinitis pigmentosa can be inherited and may present in childhood. Certain genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome, Marfan syndrome, and neurofibromatosis, can affect multiple organ systems, including the eyes. Children with these syndromes may be at higher risk for developing a range of eye problems, including refractive errors, cataracts, and retinal abnormalities.
Environmental Factors
The widespread use of digital screens and electronic devices has raised concerns about the impact on children’s eye health. Prolonged screen time can lead to digital eye strain, dry eyes, and an increased risk of myopia development in children. Exposure to environmental pollutants, allergens, and irritants can also affect children’s eye health. Airborne pollutants, such as smoke, dust, and pollen, can trigger allergic reactions and exacerbate symptoms of eye irritation and discomfort.
Behavioral Factors
Teaching children good eye care habits from a young age is essential for maintaining healthy vision. Encouraging regular breaks from screens, proper reading posture, and wearing protective eyewear during sports and outdoor activities can help prevent eye strain and reduce the risk of developing eye problems. Conversely, poor eye care habits, such as excessive screen time, inadequate sleep, and rubbing the eyes, can contribute to eye strain, dry eyes, and other vision-related issues. Addressing these habits early on can help mitigate their impact on children’s eye health and well-being.
Medical Conditions and Diseases
Certain systemic conditions, including diabetes, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, and neurofibromatosis, can present with ocular manifestations, potentially affecting the structure and function of the eyes. These conditions may lead to vision problems and other ocular complications, underscoring the importance of comprehensive eye care. In fact, eye problems in children can sometimes serve as the initial indicators of underlying health issues. Thus, regular eye exams play a pivotal role in early detection, enabling prompt intervention and management of associated health conditions. By prioritizing proactive eye health monitoring, caregivers and healthcare providers can address potential systemic concerns and ensure holistic well-being for children.
Read More: What is a Pediatric Ophthalmologist?
Diagnosis and Treatment
Early detection of eye problems is paramount for preserving vision and preventing complications. Routine eye exams, starting in infancy, can help identify issues early on and facilitate prompt intervention and treatment. Treatment options for childhood eye problems vary depending on the specific condition and its severity. Corrective lenses, such as glasses or contact lenses, may be prescribed for refractive errors. Patching therapy and vision therapy may be recommended for amblyopia and strabismus, respectively. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to correct structural abnormalities or misalignments of the eyes.
Prevention Strategies
Educating children and parents about the importance of good eye care habits is key to preventing eye problems. Encouraging regular eye exams, limiting screen time, and promoting outdoor play and physical activity can help maintain healthy vision and reduce the risk of developing eye problems. Making environmental and lifestyle modifications, such as creating a screen-free bedroom environment, minimizing exposure to allergens and pollutants, and encouraging a balanced diet rich in eye-healthy nutrients, can further support children’s eye health and well-being.
Impact on Child Development
Untreated eye problems can profoundly affect children’s academic performance, social interactions, and overall quality of life. By addressing these issues early, children can thrive both academically and socially. Moreover, childhood eye problems can have lasting implications for vision and overall well-being, underscoring the importance of timely intervention and management. Early detection and treatment are vital for preserving vision and preventing permanent vision loss or impairment, ensuring that children can enjoy a future filled with clarity and confidence in their visual abilities.
Role of Pediatric Ophthalmologist
A pediatric ophthalmologist plays a crucial role in addressing childhood eye problems comprehensively. These specialized healthcare professionals are trained to diagnose, manage, and treat a wide range of eye conditions affecting children, from infancy through adolescence. By collaborating with parents, caregivers, and other healthcare providers, pediatric ophthalmologists ensure that children receive timely screenings, accurate diagnoses, and appropriate interventions to address their eye health needs. Through comprehensive eye examinations, specialized testing, and tailored treatment plans, Children Eye Doctor helps children achieve and maintain optimal vision, enabling them to thrive academically, socially, and emotionally. Additionally, pediatric ophthalmologists play a vital role in educating parents and caregivers about preventive measures and healthy eye care habits to promote long-term eye health and well-being for children.
Final Thoughts
Childhood eye problems encompass a spectrum of conditions that can significantly impact a child’s quality of life and development. From refractive errors to more complex issues like amblyopia and strabismus, understanding the causes and implications of these conditions is paramount for early detection and intervention. Childhood eye problems can arise from a combination of developmental, genetic, environmental, behavioral, and medical factors. Understanding these factors is essential for implementing preventive measures and early interventions to safeguard children’s eye health. By raising awareness about the causes and risk factors of childhood eye problems and promoting proactive eye care practices, parents, caregivers, and healthcare providers can work together to ensure that children maintain healthy vision and enjoy a lifetime of optimal eye health.